> Use simple random sampling to select observations from a sampling frame
To use the sampling tool, select a data set where each row in the data set is unique (i.e., no duplicates). A dataset that fits these requirements is bundled with Radiant and is available through the _Data > Manage_ tab (i.e., choose `Examples` from the `Load data of type` drop-down and press `Load`). Select `rndnames` from the `Datasets` dropdown.
`Names` is a unique identifier in this dataset. If we select this variable and choose the desired sample size, e.g., 10, list of names of the desired length will be created.
How does this work? Each person in the data is assigned a random number between 0 and 1 from a uniform distribution. Rows are then sorted on that random number and the $n$ people from the list with the highest score are selected for the sample. By using a random number, every respondent has the same probability of being in the sample. For example, if we need a sample of 10 people from the 100 included in the `rndnames` dataset, each individual has a 10% chances of being included in the sample. By default, the random seed is set to `1234` to ensure the sampling results are reproducible. If there is no input in `Rnd. seed`, the selected rows will change every time we generate a sample.
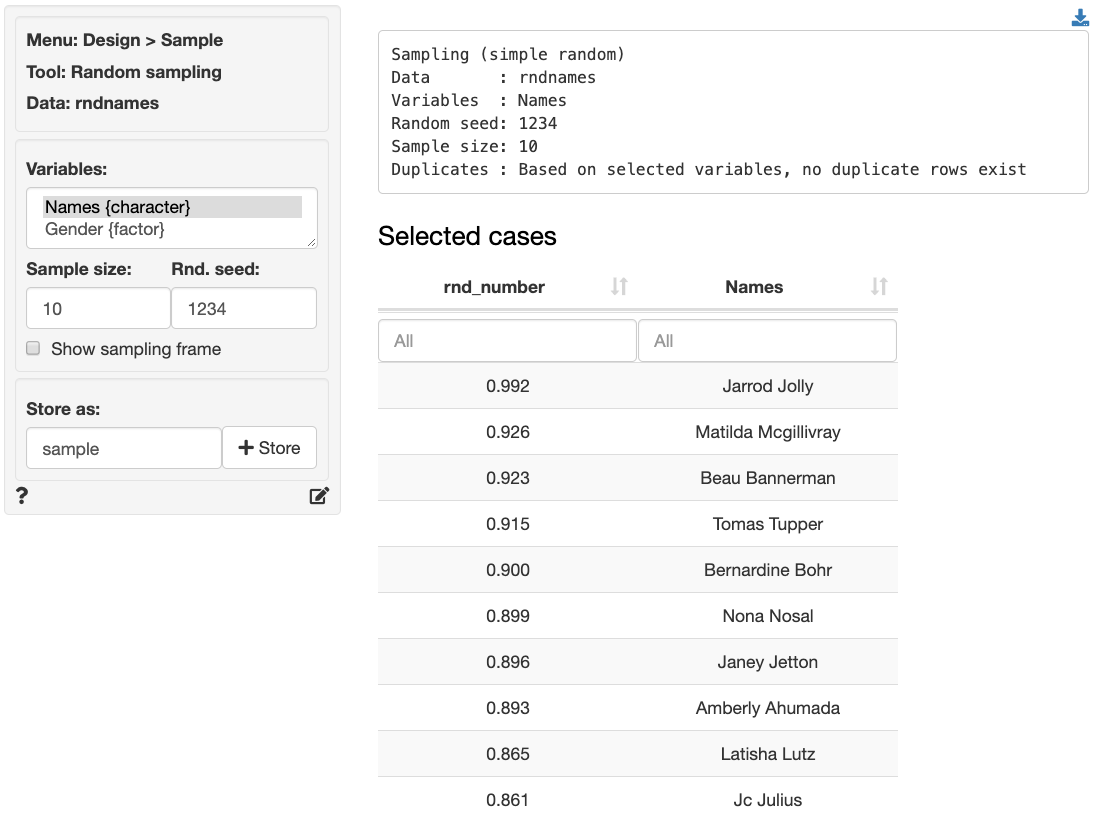
The full list of 100 people is called the `sampling frame`. Ideally, this is a comprehensive list of _all_ sampling units (e.g., customers or companies) in your target market. To determine the appropriate value for _n_, use the sample size tools in the _Design_ menu. To show the full sampling frame, click on the `Show sampling frame` check box.
To download data for the generated sample in CSV format, click on the icon in the top-right of your screen. The created sample can also be stored in Radiant by providing a name for the dataset and then clicking on the `Store` button.
### Report > Rmd
Add code to _Report > Rmd_ to (re)create the sample by clicking the icon on the bottom left of your screen or by pressing `ALT-enter` on your keyboard.
### R-functions
For an overview of related R-functions used by Radiant for sampling and sample size calculations see _Design > Sample_
The key function from the `stats` package used in the `sampling` tool is `runif`. This function is used to generate the random numbers assigned to each row in the available data.

